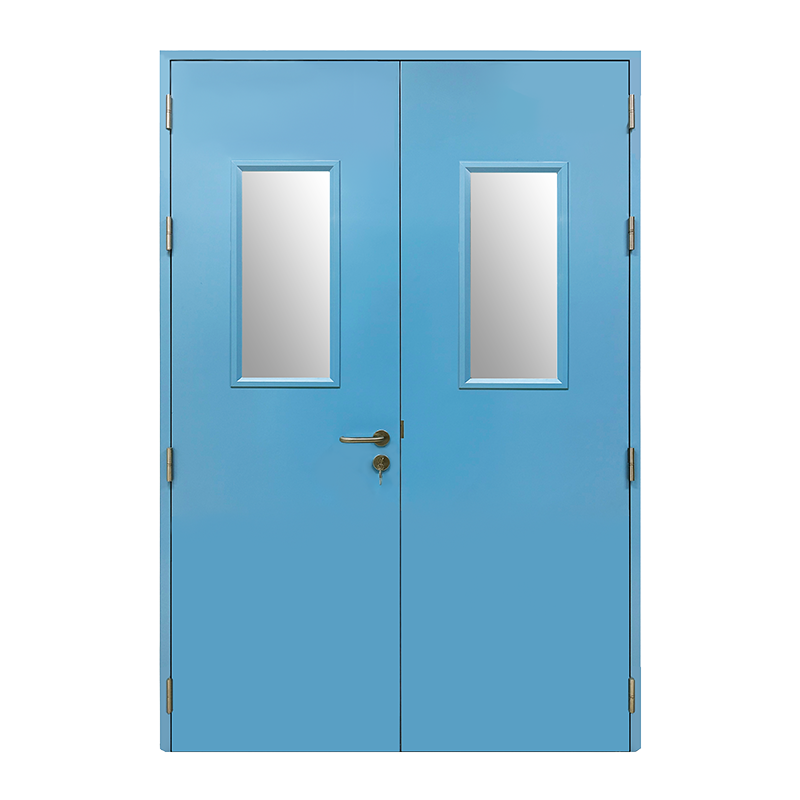
How Do I Maintain and Inspect Fire-Resistant Doors to Ensure Safety?
Fire-resistant doors are critical components in building safety. Designed to slow the spread of fire and smoke, they protect occupants, provide safe evacuation routes, and minimize property damage. However, simply installing a fire-resistant door is not enough. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure that these doors perform effectively in emergencies.
1. Understanding Fire-Resistant Doors
Before diving into maintenance and inspection, it is important to understand what fire-resistant doors are and how they work.
a) Definition and Function
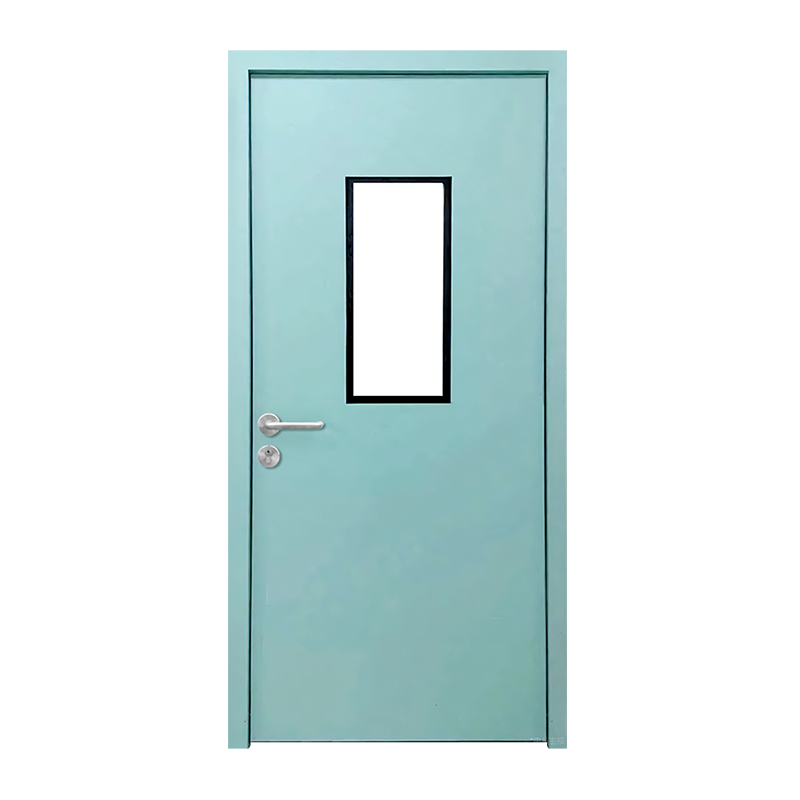
Fire-resistant doors, often referred to as fire-rated doors, are specially designed doors that can resist fire for a specified period, usually ranging from 20 minutes to 4 hours. They are constructed with fire-resistant materials such as steel, solid timber, or composite cores, often combined with intumescent seals. These seals expand when exposed to heat, preventing flames and smoke from passing through the gaps between the door and frame.
b) Key Components
- Door Leaf: The main panel, constructed to withstand fire.
- Frame: Provides structural support and holds the door securely.
- Intumescent Seals: Expand in high temperatures to seal gaps.
- Hardware: Includes hinges, handles, closers, and latches that must be fire-rated.
Understanding these components is crucial for proper inspection and maintenance, as each part plays a role in fire protection.
2. Importance of Regular Maintenance
Fire-resistant doors are only effective if they are properly maintained. Over time, wear and tear, environmental conditions, and accidental damage can compromise their performance.
a) Safety Compliance
Many jurisdictions have fire safety codes that require regular inspection and maintenance of fire-resistant doors. Failing to comply can result in legal penalties and increased liability in case of a fire.
b) Operational Reliability
A door that cannot close, latch, or seal correctly may fail during an emergency, allowing fire and smoke to spread rapidly. Regular maintenance ensures that doors operate as intended.
c) Longevity and Cost Savings
Routine maintenance extends the life of fire-resistant doors and reduces costs associated with emergency repairs or replacements.
3. Inspection Schedule
Establishing a consistent inspection schedule is critical. Fire-resistant doors should be inspected at multiple intervals:
- Monthly Visual Checks: Quick inspections to identify obvious issues such as damage, missing hardware, or blocked doors.
- Quarterly Operational Tests: Testing the door’s closing, latching, and alignment.
- Annual Comprehensive Inspection: Conducted by qualified personnel to evaluate structural integrity, hardware performance, and compliance with fire safety codes.
Having a documented schedule ensures that inspections are not missed and provides evidence of compliance.
4. Visual Inspection Checklist
A visual inspection can reveal many common issues that may compromise the effectiveness of fire-resistant doors. Key areas to check include:
a) Door Leaf and Frame
- Look for cracks, warping, or holes in the door leaf.
- Ensure the frame is securely anchored and shows no signs of damage or rust.
- Verify that the door sits properly within the frame without excessive gaps.
b) Intumescent Seals and Gaskets
- Check that seals are present along all edges and are free of damage.
- Ensure that seals are not compressed, worn, or missing, as gaps can allow fire and smoke to pass.
c) Hardware
- Inspect hinges, locks, latches, and handles for wear or damage.
- Ensure that self-closing devices are intact and properly adjusted.
- Verify that panic bars or emergency exit devices function correctly.
d) Surface Condition
- Check for paint or coatings that may cover intumescent seals or hardware.
- Look for signs of corrosion, moisture damage, or chemical exposure that could weaken materials.
5. Operational Testing
After the visual inspection, operational testing ensures that the fire-resistant door functions correctly under normal use. Key steps include:
a) Door Closing
- Open the door fully and release it. The door should close smoothly without sticking or dragging.
- Check that the self-closing device allows the door to close completely.
b) Latching and Locking
- Ensure the door latches securely when closed. A door that does not latch properly can compromise fire resistance.
- Test locking mechanisms and panic devices to confirm proper function.
c) Alignment and Gap Measurement
- Measure the gaps around the door leaf. Typically, gaps should not exceed fire safety code specifications (often 3–4 mm at the sides and top).
- Adjust hinges or frames if gaps are excessive to maintain an effective seal during a fire.

6. Maintenance Procedures
Proper maintenance involves correcting identified issues, lubricating moving parts, and replacing worn components.
a) Door Leaf and Frame
- Repair cracks, warping, or dents using materials recommended for fire-rated doors.
- Repaint or refinish surfaces to prevent corrosion, ensuring coatings do not interfere with seals.
b) Intumescent Seals
- Replace damaged or missing seals promptly.
- Clean seals to remove dust, debris, or paint that may prevent expansion during a fire.
c) Hardware Maintenance
- Lubricate hinges, locks, and closers with suitable fire-rated lubricants.
- Tighten screws and bolts, and replace worn or damaged hardware with fire-rated equivalents.
- Adjust self-closing devices to ensure proper speed and pressure.
d) Documentation
- Record all maintenance activities, including repairs and replacements.
- Maintain inspection logs to demonstrate compliance with safety codes and standards.
7. Common Issues and How to Address Them
Awareness of frequent problems helps prevent door failure. Common issues include:
- Sticking or Misaligned Doors: Usually caused by frame warping or loose hinges; adjust or repair the frame.
- Damaged Intumescent Seals: Replace damaged seals immediately to maintain fire resistance.
- Faulty Self-Closers: Adjust or replace devices to ensure doors close completely.
- Corroded Hardware: Clean or replace components, particularly in humid or industrial environments.
Regular inspections help catch these issues early, avoiding costly replacements and safety risks.
8. Compliance and Certification
Fire-resistant doors must meet national or regional fire safety standards, such as NFPA 80 in the United States or EN 1634 in Europe. Maintaining compliance involves:
- Ensuring that doors retain their original fire rating after any repair or modification.
- Using certified replacement parts, including seals and hardware.
- Documenting inspections and maintenance to provide proof of adherence to regulations.
Failure to comply with these standards can not only compromise safety but may also result in legal liability.
9. Tips for Facility Managers and Owners
To ensure effective fire door maintenance:
- Train Staff: Educate personnel on the importance of fire door safety and inspection procedures.
- Schedule Regular Inspections: Use reminders or maintenance software to track inspection dates.
- Keep Records: Maintain logs for inspections, repairs, and replacements.
- Avoid Obstructions: Ensure doors are never propped open or blocked.
- Use Qualified Personnel: Hire certified technicians for annual inspections and major maintenance.
Proactive management reduces risk, ensures compliance, and enhances overall building safety.
Conclusion
Fire-resistant doors are vital for life safety and property protection, but their effectiveness depends on proper maintenance and inspection. Regular visual inspections, operational testing, timely repairs, and adherence to fire safety codes are all essential components of a robust maintenance program. By following the steps outlined in this guide, facility managers and building owners can ensure that fire-resistant doors continue to provide reliable protection in the event of a fire.
Maintaining these doors is not just a legal obligation—it is a critical safety measure that safeguards lives, limits property damage, and ensures that buildings meet modern fire safety standards. With consistent attention, training, and documentation, fire-resistant doors can continue to serve their purpose effectively for many years.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский عربى
عربى