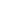Steel Cleanroom Door: A high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and airtight cleanroom isolation solution
Product Overview
Steel cleanroom door is a specialized type of industrial door designed specifically for environments where air purity, hygiene, and contamination control are critical. These doors form an essential part of cleanroom architecture, acting not only as entry and exit points but also as critical barriers that help maintain the required cleanliness levels inside controlled environments.
Unlike conventional commercial or residential doors, steel cleanroom doors are engineered to meet stringent technical standards, ensuring high durability, superior sealing performance, and resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and mechanical wear. Their design is tailored to withstand frequent use in environments where every detail—down to the smallest particle—matters.
The Role of Steel Doors in Cleanroom Systems
Cleanrooms are controlled spaces where airborne particle concentration, temperature, humidity, and air pressure are maintained within defined limits. These spaces are crucial in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, microelectronics, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
In these settings, a door is not simply a mechanical structure for opening and closing—it is a component of the contamination control system. Steel cleanroom doors act as a physical barrier, separating the clean environment from less controlled areas. They contribute to:
Particle containment: Preventing particles from entering or leaving the cleanroom during operations.
Air pressure management: Supporting the maintenance of positive or negative pressure differentials between spaces.
Environmental stability: Helping regulate temperature and humidity by limiting uncontrolled airflow.
Because the door interacts directly with the airflow, filtration systems, and personnel movement, its design and construction must integrate seamlessly with the overall cleanroom architecture.
Material Advantages of Steel in Cleanroom Applications
Steel is widely chosen for cleanroom door construction because of its mechanical strength, durability, and adaptability. The most common choice is galvanized steel or powder-coated steel, both of which offer a robust surface resistant to wear and environmental exposure.
Key advantages include:
High structural strength: Steel resists bending, warping, and deformation, even with frequent use or exposure to varying environmental conditions.
Impact resistance: Cleanroom doors often endure contact from carts, trolleys, and equipment; steel provides reliable protection against dents and damage.
Longevity: With proper surface treatment (e.g., powder coating or epoxy paint), steel cleanroom doors can perform reliably for decades.
Customizability: Steel can be fabricated into a wide range of sizes, shapes, and configurations, supporting single-leaf, double-leaf, and sliding designs.
When compared to materials like HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) or aluminum, steel offers a superior combination of rigidity and mechanical performance—particularly for environments with heavy equipment traffic.
Compliance with Cleanroom Standards
Steel cleanroom doors are designed to meet strict industry standards, such as:
ISO 14644: International cleanroom classification based on airborne particle concentration.
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice): Regulatory guidelines for pharmaceutical and food production.
EN and ASTM standards: Covering aspects such as fire resistance, impact strength, and corrosion resistance.
For example, in a pharmaceutical production facility, steel cleanroom doors may need to withstand daily disinfection with alcohol-based solutions or chemical detergents without losing integrity. Their smooth, non-porous surfaces are easy to clean and resistant to microbial growth, ensuring compliance with hygiene protocols.
Structural Design Features
Steel cleanroom doors are engineered with features that optimize performance in controlled environments:
Seamless surface finishes: Minimizing joints and crevices where dust and bacteria can accumulate.
Flush window integration: When observation windows are included, they are flush-mounted and sealed to prevent contamination traps.
Specialized sealing systems: Perimeter gaskets and bottom sweeps maintain airtightness, reducing particle infiltration.
Adjustable frame systems: Allowing for perfect alignment during installation, which is critical for maintaining seal integrity.
In many designs, steel door panels are filled with core materials such as honeycomb aluminum, mineral wool, or polyurethane foam. These cores improve the door’s thermal insulation, acoustic performance, and impact resistance.
Variations and Customization
Steel cleanroom doors come in multiple configurations to suit different operational needs:
Single-leaf hinged doors: Standard for personnel entry points.
Double-leaf hinged doors: For larger equipment transfer or heavy traffic.
Sliding steel cleanroom doors: Ideal for saving space and minimizing airflow disturbance.
Automatic doors: Equipped with sensors for touch-free operation, reducing contamination risks.
Customization options extend to:
Dimensions: Width, height, and thickness tailored to project specifications.
Opening direction: Left-hand, right-hand, or reversible.
Surface finish: Powder coating, epoxy, or stainless-steel cladding for enhanced durability.
Accessories: Integrated windows, electronic locks, panic bars, and interlock systems.
Industry Applications
Steel cleanroom doors are used in a broad range of industries:
Pharmaceutical manufacturing: To maintain strict hygiene and GMP compliance.
Biotechnology labs: For controlled experiments and sensitive production processes.
Microelectronics: To protect components from dust, static, and contamination.
Aerospace assembly areas: For precision manufacturing with tight environmental controls.
Hospitals and surgical suites: To reduce infection risks and control sterile areas.
In all these industries, the door must perform consistently under high-traffic conditions while maintaining strict cleanliness and environmental separation.
Integration with Cleanroom Systems
An effective steel cleanroom door is not an isolated product—it works as part of a larger contamination control strategy. This includes:
Airlocks and pass-throughs: Doors that work in pairs to minimize pressure loss during entry/exit.
Interlocking systems: Preventing two doors from opening simultaneously in critical areas.
Automation integration: Synchronizing door operation with air handling and filtration systems.
Because of these integrations, the selection of a steel cleanroom door should involve both the facility designer and the cleanroom engineering team.
The Strategic Importance of Quality Doors
Choosing the right steel cleanroom door is not only about durability and appearance; it is about safeguarding the integrity of the cleanroom itself. An improperly sealed, poorly constructed, or misaligned door can undermine the entire cleanroom performance, leading to costly downtime, regulatory violations, and potential product contamination.
Therefore, manufacturers invest in precision engineering, rigorous testing, and compliance documentation to ensure every steel cleanroom door meets the demanding requirements of modern industry.
Core Features and Advantages
Steel cleanroom doors are not just ordinary doors made of metal; they are precision-engineered components designed to perform consistently under the demanding conditions of controlled environments. Their core features address three fundamental cleanroom challenges: contamination control, operational efficiency, and durability. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the primary features and the advantages they deliver.
High Structural Strength
One of the most compelling reasons for choosing a steel cleanroom door is its inherent mechanical strength. Steel, especially in the form of galvanized or cold-rolled sheet, offers exceptional resistance to bending, warping, and deformation.
Key advantages:
Long-term dimensional stability: Even after years of frequent opening and closing, steel doors retain their original shape and alignment.
Impact resistance: In high-traffic cleanrooms, equipment such as trolleys or carts may accidentally hit the door. Steel doors are better able to withstand such impacts without denting or cracking.
Enhanced safety: A robust structure minimizes the risk of accidental breaches that could compromise the cleanroom’s controlled environment.
This strength is particularly important for cleanrooms in pharmaceutical and electronic manufacturing, where continuous use can stress weaker materials like laminate or aluminum.
Excellent Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Cleanroom environments often require daily cleaning and disinfection using alcohol-based solutions, chlorine agents, or other chemical detergents. Without proper resistance, door surfaces can deteriorate quickly.
Steel cleanroom doors are designed to resist:
Oxidation and rust: Through galvanization or stainless-steel cladding.
Chemical attack: Powder-coated or epoxy-painted surfaces protect against harsh cleaning chemicals.
Moisture damage: Especially important in facilities with humidity-controlled rooms or wet cleaning processes.
For applications in biotechnology or food processing, where frequent sanitation is mandatory, corrosion resistance ensures that the door maintains its integrity and hygiene standards over time.
Superior Airtightness and Sealing Performance
In cleanrooms, controlling airflow is critical. Steel cleanroom doors incorporate specialized sealing systems that ensure minimal air leakage.
Sealing technologies include:
High-quality EPDM or silicone gaskets around the door frame and leaf.
Drop-down seals or automatic bottom seals that engage when the door is closed.
Flush fit designs that eliminate gaps between the door and frame.
These sealing features help:
Maintain positive pressure to keep contaminants out.
Maintain negative pressure for isolation rooms or containment labs.
Reduce energy costs by preventing conditioned air from escaping.
The result is a stable, controlled environment that supports cleanroom classification compliance.
Hygienic and Easy-to-Clean Surfaces
Steel cleanroom doors are designed to be as smooth and seamless as possible to minimize particle accumulation.
Hygienic design elements:
Flush glazing for observation windows to prevent dirt traps.
Minimal joints and seams to reduce microbial growth areas.
Powder-coated finishes that resist stains and are simple to wipe down.
In industries like pharmaceuticals, every surface is evaluated for ease of cleaning. A steel door with a seamless finish shortens cleaning cycles while ensuring thorough sanitation.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Many cleanroom facilities require fire-rated barriers to protect valuable equipment, sensitive processes, and personnel in case of emergencies. Steel doors naturally provide higher fire resistance compared to materials like aluminum or PVC.
Benefits:
Compliance with EN 1634-1 or ASTM E119 fire testing standards.
Ability to act as both a contamination barrier and a fire safety barrier.
Integration with fire alarm systems for automatic closing.
This dual functionality makes steel cleanroom doors ideal for multi-risk environments.
Noise and Thermal Insulation
While the main function of a cleanroom door is contamination control, modern steel cleanroom doors can also improve acoustic comfort and thermal regulation.
How this is achieved:
Insulated cores (e.g., mineral wool, honeycomb aluminum, or polyurethane) dampen sound transmission.
Thermal insulation reduces temperature fluctuations between areas, supporting climate control systems.
These features benefit environments like hospital operating rooms or microelectronics labs, where stable conditions are crucial.
Customization and Design Flexibility
One of the strengths of steel as a material is its adaptability. Steel cleanroom doors can be tailored to suit the specific functional and aesthetic needs of a facility.
Customizable aspects:
Size and dimensions for non-standard openings.
Opening type: single-leaf, double-leaf, or sliding.
Surface finish: epoxy paint, powder coating, or stainless steel.
Color matching for facility branding or zoning purposes.
Hardware and accessories: locks, panic bars, automatic closers, interlocking systems, and electronic access control.
Such customization ensures the door not only meets technical requirements but also integrates harmoniously with the facility’s overall layout.
Compatibility with Automation
Touchless operation is increasingly important in cleanrooms to minimize contact points and reduce contamination risks.
Automation-ready features:
Sensor-activated opening systems.
Integration with access control and personnel tracking.
Interlocking mechanisms to prevent multiple doors from opening simultaneously in airlocks.
These capabilities not only improve hygiene but also streamline workflow in high-traffic areas.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
While steel cleanroom doors may require a higher initial investment compared to some other materials, their durability and performance deliver long-term savings.
Cost advantages over time:
Lower maintenance costs due to robust construction.
Reduced downtime from fewer repairs or replacements.
Better energy efficiency through superior sealing performance.
In industries where contamination incidents can result in significant financial losses, investing in a high-quality steel cleanroom door is a preventive measure.
Compliance and Certification
Most reputable steel cleanroom door manufacturers provide documentation and testing reports to demonstrate compliance with relevant standards.
Common certifications include:
ISO cleanroom class compatibility.
GMP compliance documentation.
Fire-resistance test reports.
Air leakage test results.
These certifications not only reassure facility managers but also help during audits and regulatory inspections.
Summary of Advantages
Steel cleanroom doors offer a unique combination of strength, hygiene, airtightness, and customization that makes them suitable for a wide range of controlled environments. Their ability to maintain performance under rigorous use, withstand chemical cleaning, and integrate with automation systems positions them as a high-value investment for any cleanroom project.
In short, the decision to use steel cleanroom doors is about more than just material selection—it is about ensuring the stability, compliance, and long-term functionality of a facility’s controlled environment.
Main Types of Steel Cleanroom Doors
Steel cleanroom doors are not a one-size-fits-all product. Different industries, facility layouts, and operational processes require specific door configurations to achieve optimal cleanliness, safety, and workflow efficiency. While all steel cleanroom doors share the same fundamental purpose—maintaining the integrity of controlled environments—they vary significantly in form, function, and features.
Below is a detailed overview of the main types of steel cleanroom doors, along with their design characteristics, advantages, and typical applications.
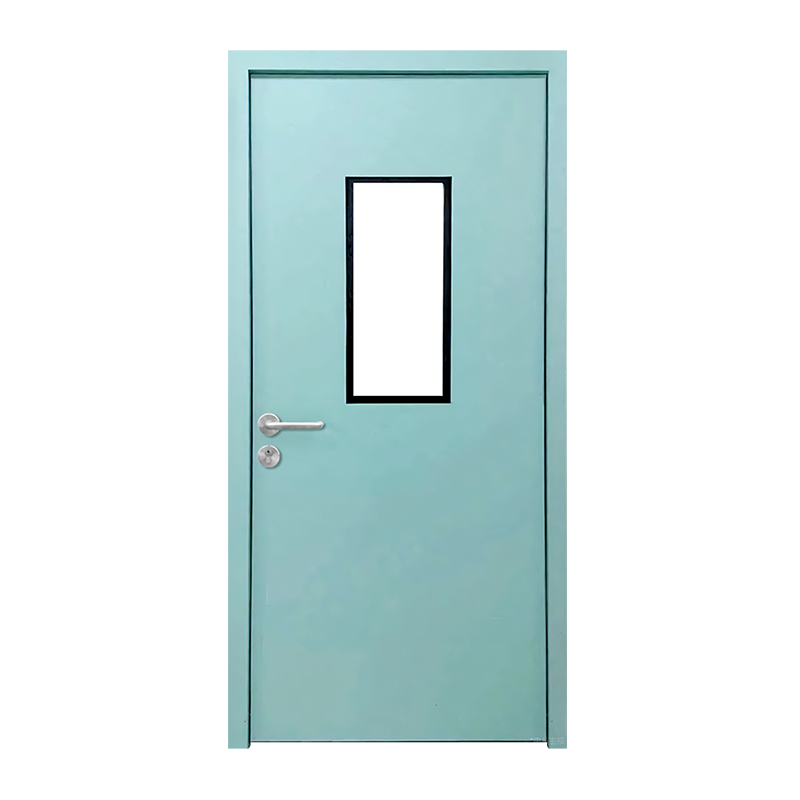
Single-Leaf Hinged Steel Cleanroom Doors
Description:
The most common configuration, single-leaf hinged doors feature one door panel attached to the frame via hinges. They can be designed to swing inward or outward, depending on the cleanroom’s pressure differential and traffic flow requirements.
Key Features:
Available in both left-hand and right-hand opening orientations.
Typically equipped with continuous stainless-steel hinges or heavy-duty pivot hinges for smooth operation.
Often include a flush observation window to allow visual monitoring without opening the door.
Advantages:
Simple, reliable mechanism with minimal maintenance requirements.
Strong sealing capability due to a single leaf and fewer potential leakage points.
Ideal for personnel entry and exit in small to medium-sized rooms.
Typical Applications:
Pharmaceutical labs and packaging rooms.
Electronics assembly areas.
Research laboratories requiring controlled access.
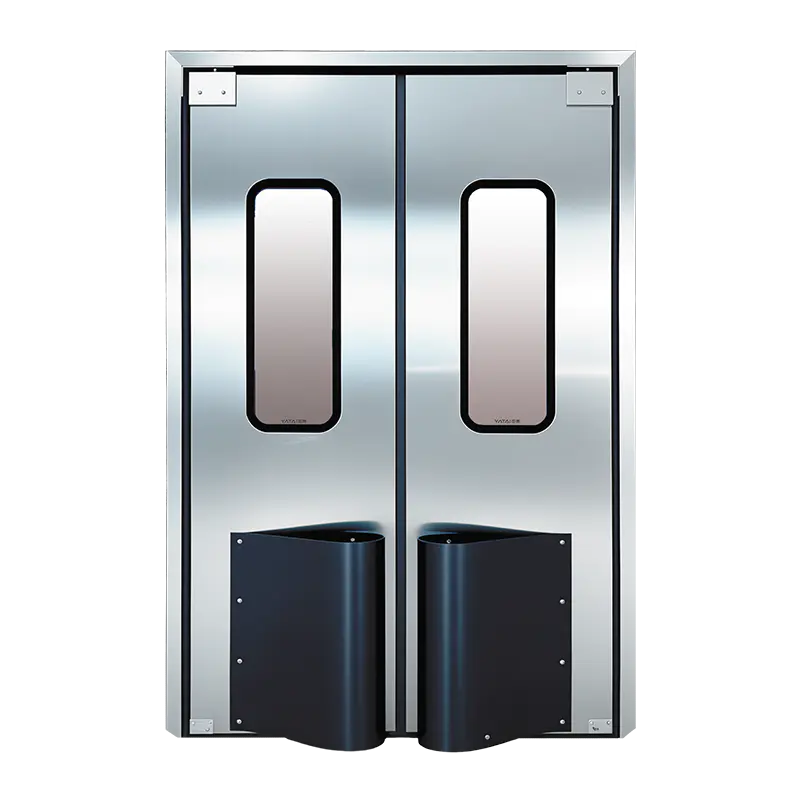
Double-Leaf Hinged Steel Cleanroom Doors
Description:
These doors have two panels that swing open, allowing a much wider passageway. The two leaves can be symmetrical (equal size) or asymmetrical (one larger than the other).
Key Features:
Central meeting stile with sealing gaskets to maintain airtightness when closed.
One leaf may be fixed (inactive) and can be unlocked for equipment transfer.
Heavy-duty door closers or concealed floor springs for smooth closure.
Advantages:
Wide opening suitable for moving large equipment or materials.
Flexible operation—use one leaf for regular traffic, both leaves for large transfers.
Retains cleanroom sealing performance when both leaves are properly closed.
Typical Applications:
Airlock entry for manufacturing areas.
Areas where equipment carts, trolleys, or large machinery must be moved.
Food processing plants with large-scale production equipment.
Sliding Steel Cleanroom Doors
Description:
Instead of swinging open, sliding doors move horizontally along a track. They can be manual or motorized.
Key Features:
Mounted on an overhead or recessed track system for smooth sliding.
Can be single sliding (one leaf moves) or double sliding (two leaves slide apart).
Sealing achieved via edge gaskets and track-side compression seals.
Advantages:
Space-saving—ideal for narrow corridors or areas with limited clearance.
Minimizes air turbulence compared to swinging doors.
Easy to automate for touchless operation.
Typical Applications:
Hospital operating rooms.
Semiconductor fabrication cleanrooms.
High-traffic corridors where opening space is limited.
Automatic Steel Cleanroom Doors
Description:
Automatic doors use motorized systems to open and close without manual contact. They can be either sliding or hinged.
Key Features:
Operated via motion sensors, push buttons, or access control systems.
Can be integrated with interlock systems to prevent simultaneous opening of multiple doors.
Often include safety sensors to prevent accidental closure on people or equipment.
Advantages:
Reduces touchpoints, minimizing contamination risks.
Improves efficiency for high-traffic areas.
Allows hands-free operation, beneficial for personnel carrying equipment.
Typical Applications:
Pharmaceutical production airlocks.
Clean corridors in microelectronics facilities.
Hospital sterile zones.
Steel Cleanroom Doors with Observation Windows
Description:
These are standard steel cleanroom doors (single or double leaf) equipped with a flush-mounted window to allow visual communication between rooms without opening the door.
Key Features:
Double-glazed or laminated glass for insulation and safety.
Flush mounting prevents dust accumulation on edges.
Glass may have anti-fog or anti-static coatings.
Advantages:
Enhances safety by allowing visibility before opening the door.
Supports workflow coordination without compromising cleanliness.
Maintains full airtightness with proper sealing.
Typical Applications:
Hospital isolation rooms.
Semiconductor assembly lines.
Pharmaceutical quality control labs.
Fire-Rated Steel Cleanroom Doors
Description:
These doors combine cleanroom sealing performance with certified fire resistance.
Key Features:
Multi-layer construction with fire-resistant core materials such as mineral wool.
Fire ratings typically range from 30 to 120 minutes.
Integrated with fire alarm systems for automatic closure during emergencies.
Advantages:
Dual function—contamination control and fire safety.
Regulatory compliance for facilities handling flammable substances.
Robust construction without compromising cleanroom performance.
Typical Applications:
Pharmaceutical storage rooms with flammable chemicals.
Electronic manufacturing areas requiring fire compartmentalization.
Medical laboratories handling volatile substances.
Specialized and Custom Steel Cleanroom Doors
In addition to the common configurations, some facilities require highly specialized designs to meet unique operational demands.
Examples:
Pass-through steel cleanroom doors: For transferring materials between rooms while minimizing personnel movement.
Hermetically sealed steel doors: Used in high-containment biosafety labs.
Radiation-shielded steel doors: For use in medical imaging or nuclear facilities.
Customization Options:
Size and thickness adjustments.
Custom coatings for specific chemical resistance.
Integration with biometric access systems.
Enhanced acoustic insulation for noise-sensitive environments.
Choosing the Right Type
Selecting the appropriate type of steel cleanroom door depends on several factors:
1. Traffic type and frequency: Personnel vs. equipment movement.
2. Space constraints: Whether there’s clearance for swing doors or a need for sliding.
3. Cleanroom classification: Higher classes may require more advanced sealing systems.
4. Safety requirements: Need for fire resistance, explosion protection, or impact resistance.
5. Automation needs: Whether touchless operation is necessary for contamination control.
Conclusion of This Section
The diversity of steel cleanroom door types ensures that every facility—from small laboratories to large-scale manufacturing plants—can find a solution that matches its operational needs, safety requirements, and space limitations. Whether it’s a single-leaf hinged door for a lab entry or an automated sliding door for a busy hospital corridor, each design is rooted in the same core principles: contamination prevention, durability, and seamless integration with cleanroom systems.
Application Scenarios
Steel cleanroom doors are essential in a variety of industries where contamination control, safety, and durability are critical. While their core design principles remain consistent—airtight sealing, chemical resistance, and hygienic surfaces—the specific application of these doors can vary significantly depending on the sector’s unique operational demands.
Below, we explore how steel cleanroom doors are applied across major industries, along with their performance requirements and benefits in each context.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Overview:
In the pharmaceutical industry, cleanrooms are indispensable for producing medicines, vaccines, and other healthcare products under strict Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines. Even the smallest contamination can compromise product safety and lead to regulatory non-compliance.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Maintain air pressure differentials between rooms of varying cleanliness levels.
Provide a chemical-resistant surface for frequent disinfection with alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, or chlorine-based cleaners.
Support controlled access with interlocking systems to prevent simultaneous opening of connected rooms.
Typical Applications:
Production zones: Single-leaf or double-leaf hinged doors for personnel and equipment movement.
Airlocks: Automatic doors with interlocks to control entry.
Packaging areas: Sliding doors for smooth and space-efficient operation.
Key Advantages:
High resistance to microbial growth due to non-porous steel surfaces.
Easy-to-clean design reduces downtime during sanitation cycles.
Fire-rated options enhance safety in facilities storing flammable chemicals.
Biotechnology and Life Sciences
Overview:
Biotech facilities often handle sensitive biological materials, including cell cultures, genetic samples, and biohazardous agents. These environments demand strict contamination control, often exceeding standard cleanroom requirements.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Provide hermetic sealing in biosafety level (BSL) laboratories to prevent airborne pathogen escape.
Allow safe observation through flush-mounted, double-glazed windows.
Integrate with air shower systems for personnel decontamination.
Typical Applications:
BSL-3 and BSL-4 labs: Hermetically sealed steel doors with reinforced frames.
Research labs: Single-leaf doors for individual lab rooms.
Sample storage areas: Fire-rated doors for biohazard containment.
Key Advantages:
Strong structural integrity for high-security containment.
Chemical-resistant surfaces for aggressive cleaning agents.
Compatibility with automated entry systems to reduce manual contact.
Microelectronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Overview:
Semiconductor fabrication facilities (fabs) require some of the most stringent cleanroom conditions in the world, often operating at ISO Class 5 or better. Even microscopic dust can ruin expensive wafers.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Minimize air turbulence by using sliding or automatic operation.
Maintain strict pressure differentials to prevent particle migration.
Enable pass-through access without compromising cleanliness.
Typical Applications:
Clean corridors: Automatic sliding doors for high personnel traffic.
Material transfer rooms: Double-leaf hinged doors for large equipment.
Equipment service bays: Fire-rated steel doors for safety compliance.
Key Advantages:
Exceptional sealing performance to maintain low particle counts.
Anti-static coatings to reduce electrostatic discharge (ESD) risks.
Long service life under continuous operation.
Food Processing and Packaging
Overview:
Food manufacturing facilities must comply with strict hygiene regulations to prevent contamination and ensure product safety. Cleanrooms are often used for high-risk processes such as ready-to-eat food packaging.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Provide moisture resistance in washdown areas.
Withstand temperature variations between refrigerated and ambient zones.
Support quick and easy cleaning with high-pressure water or steam.
Typical Applications:
Processing rooms: Double-leaf doors for large-scale equipment.
Cold storage areas: Insulated steel doors for temperature control.
Packaging zones: Single-leaf or sliding doors for personnel flow.
Key Advantages:
Corrosion-resistant coatings prevent rust in humid environments.
Smooth surfaces reduce the risk of bacterial harboring.
Thermal insulation improves energy efficiency in chilled areas.
Aerospace and Precision Engineering
Overview:
Aerospace manufacturing involves the assembly of complex components that require dust-free environments to ensure performance and reliability.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Create controlled access points for large assemblies.
Maintain temperature and humidity stability in production bays.
Integrate with specialized security systems for restricted areas.
Typical Applications:
Assembly cleanrooms: Oversized double-leaf hinged or sliding steel doors.
Testing labs: Fire-rated doors to protect sensitive instruments.
Parts storage areas: Secure steel doors with electronic access control.
Key Advantages:
High durability for long-term industrial use.
Ability to accommodate large custom dimensions.
Enhanced safety with fire and impact resistance.
Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities
Overview:
In medical environments, infection prevention is paramount. Cleanroom-grade doors are used in surgical theaters, isolation rooms, and sterile supply areas.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Act as infection control barriers between sterile and non-sterile areas.
Support hands-free operation to minimize contamination.
Provide sound insulation for patient comfort.
Typical Applications:
Operating rooms: Automatic sliding doors for sterile entry.
Isolation wards: Hermetically sealed hinged doors.
Sterile storage areas: Single-leaf hinged doors with observation windows.
Key Advantages:
Easy-to-clean, antimicrobial powder coatings.
Airtight seals prevent airborne pathogen spread.
Smooth, silent operation for a calm environment.
Research and Testing Laboratories
Overview:
These facilities vary widely, from chemical analysis labs to environmental testing rooms. Cleanroom doors must adapt to different safety and cleanliness standards.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Provide chemical resistance for labs handling solvents and reagents.
Offer secure locking systems for sensitive research areas.
Facilitate controlled material transfer between zones.
Typical Applications:
Chemical testing labs: Fire-rated and corrosion-resistant doors.
Material science labs: Double-leaf hinged doors for large sample movement.
Environmental chambers: Insulated steel doors for climate control.
Key Advantages:
Resistance to spills and chemical splashes.
Long-term performance under heavy usage.
Flexible customization for unique laboratory layouts.
Why Steel is the Preferred Choice Across Industries
Across all these scenarios, steel cleanroom doors consistently deliver:
Superior durability under high-frequency use.
Unmatched sealing performance to maintain cleanliness.
Versatile customization to fit sector-specific requirements.
Regulatory compliance with international standards like ISO 14644 and GMP.
In short, whether the priority is preventing contamination in a biotech lab, controlling humidity in a food plant, or providing security in an aerospace facility, steel cleanroom doors remain the most dependable solution.
Application Scenarios
Steel cleanroom doors are essential in a variety of industries where contamination control, safety, and durability are critical. While their core design principles remain consistent—airtight sealing, chemical resistance, and hygienic surfaces—the specific application of these doors can vary significantly depending on the sector’s unique operational demands.
Below, we explore how steel cleanroom doors are applied across major industries, along with their performance requirements and benefits in each context.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Overview:
In the pharmaceutical industry, cleanrooms are indispensable for producing medicines, vaccines, and other healthcare products under strict Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines. Even the smallest contamination can compromise product safety and lead to regulatory non-compliance.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Maintain air pressure differentials between rooms of varying cleanliness levels.
Provide a chemical-resistant surface for frequent disinfection with alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, or chlorine-based cleaners.
Support controlled access with interlocking systems to prevent simultaneous opening of connected rooms.
Typical Applications:
Production zones: Single-leaf or double-leaf hinged doors for personnel and equipment movement.
Airlocks: Automatic doors with interlocks to control entry.
Packaging areas: Sliding doors for smooth and space-efficient operation.
Key Advantages:
High resistance to microbial growth due to non-porous steel surfaces.
Easy-to-clean design reduces downtime during sanitation cycles.
Fire-rated options enhance safety in facilities storing flammable chemicals.
Biotechnology and Life Sciences
Overview:
Biotech facilities often handle sensitive biological materials, including cell cultures, genetic samples, and biohazardous agents. These environments demand strict contamination control, often exceeding standard cleanroom requirements.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Provide hermetic sealing in biosafety level (BSL) laboratories to prevent airborne pathogen escape.
Allow safe observation through flush-mounted, double-glazed windows.
Integrate with air shower systems for personnel decontamination.
Typical Applications:
BSL-3 and BSL-4 labs: Hermetically sealed steel doors with reinforced frames.
Research labs: Single-leaf doors for individual lab rooms.
Sample storage areas: Fire-rated doors for biohazard containment.
Key Advantages:
Strong structural integrity for high-security containment.
Chemical-resistant surfaces for aggressive cleaning agents.
Compatibility with automated entry systems to reduce manual contact.
Microelectronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Overview:
Semiconductor fabrication facilities (fabs) require some of the most stringent cleanroom conditions in the world, often operating at ISO Class 5 or better. Even microscopic dust can ruin expensive wafers.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Minimize air turbulence by using sliding or automatic operation.
Maintain strict pressure differentials to prevent particle migration.
Enable pass-through access without compromising cleanliness.
Typical Applications:
Clean corridors: Automatic sliding doors for high personnel traffic.
Material transfer rooms: Double-leaf hinged doors for large equipment.
Equipment service bays: Fire-rated steel doors for safety compliance.
Key Advantages:
Exceptional sealing performance to maintain low particle counts.
Anti-static coatings to reduce electrostatic discharge (ESD) risks.
Long service life under continuous operation.
Food Processing and Packaging
Overview:
Food manufacturing facilities must comply with strict hygiene regulations to prevent contamination and ensure product safety. Cleanrooms are often used for high-risk processes such as ready-to-eat food packaging.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Provide moisture resistance in washdown areas.
Withstand temperature variations between refrigerated and ambient zones.
Support quick and easy cleaning with high-pressure water or steam.
Typical Applications:
Processing rooms: Double-leaf doors for large-scale equipment.
Cold storage areas: Insulated steel doors for temperature control.
Packaging zones: Single-leaf or sliding doors for personnel flow.
Key Advantages:
Corrosion-resistant coatings prevent rust in humid environments.
Smooth surfaces reduce the risk of bacterial harboring.
Thermal insulation improves energy efficiency in chilled areas.
Aerospace and Precision Engineering
Overview:
Aerospace manufacturing involves the assembly of complex components that require dust-free environments to ensure performance and reliability.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Create controlled access points for large assemblies.
Maintain temperature and humidity stability in production bays.
Integrate with specialized security systems for restricted areas.
Typical Applications:
Assembly cleanrooms: Oversized double-leaf hinged or sliding steel doors.
Testing labs: Fire-rated doors to protect sensitive instruments.
Parts storage areas: Secure steel doors with electronic access control.
Key Advantages:
High durability for long-term industrial use.
Ability to accommodate large custom dimensions.
Enhanced safety with fire and impact resistance.
Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities
Overview:
In medical environments, infection prevention is paramount. Cleanroom-grade doors are used in surgical theaters, isolation rooms, and sterile supply areas.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Act as infection control barriers between sterile and non-sterile areas.
Support hands-free operation to minimize contamination.
Provide sound insulation for patient comfort.
Typical Applications:
Operating rooms: Automatic sliding doors for sterile entry.
Isolation wards: Hermetically sealed hinged doors.
Sterile storage areas: Single-leaf hinged doors with observation windows.
Key Advantages:
Easy-to-clean, antimicrobial powder coatings.
Airtight seals prevent airborne pathogen spread.
Smooth, silent operation for a calm environment.
Research and Testing Laboratories
Overview:
These facilities vary widely, from chemical analysis labs to environmental testing rooms. Cleanroom doors must adapt to different safety and cleanliness standards.
Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors:
Provide chemical resistance for labs handling solvents and reagents.
Offer secure locking systems for sensitive research areas.
Facilitate controlled material transfer between zones.
Typical Applications:
Chemical testing labs: Fire-rated and corrosion-resistant doors.
Material science labs: Double-leaf hinged doors for large sample movement.
Environmental chambers: Insulated steel doors for climate control.
Key Advantages:
Resistance to spills and chemical splashes.
Long-term performance under heavy usage.
Flexible customization for unique laboratory layouts.
Why Steel is the Preferred Choice Across Industries
Across all these scenarios, steel cleanroom doors consistently deliver:
Superior durability under high-frequency use.
Unmatched sealing performance to maintain cleanliness.
Versatile customization to fit sector-specific requirements.
Regulatory compliance with international standards like ISO 14644 and GMP.
In short, whether the priority is preventing contamination in a biotech lab, controlling humidity in a food plant, or providing security in an aerospace facility, steel cleanroom doors remain the most dependable solution.
Steel cleanroom doors are a critical component in maintaining the integrity, safety, and efficiency of controlled environments across industries. Their robust construction, airtight sealing, and corrosion-resistant surfaces make them ideal for applications ranging from pharmaceutical manufacturing and biotechnology to electronics, food processing, aerospace, and healthcare. By selecting the appropriate type—hinged, sliding, automatic, or fire-rated—facilities can address specific operational requirements such as personnel flow, equipment transfer, contamination control, and emergency safety.
Beyond functionality, steel cleanroom doors offer flexibility in customization. Options for glazing, automation, coatings, and specialized hardware allow them to meet unique industry standards while enhancing workflow efficiency and safety. Their durability ensures long-term performance even under high-traffic and high-frequency cleaning conditions, making them a reliable investment for any cleanroom facility.
In essence, steel cleanroom doors are not just entryways—they are integral to maintaining controlled environments, safeguarding products and personnel, and supporting regulatory compliance. By understanding the types, applications, and benefits of these doors, industries can make informed decisions that optimize both cleanliness and operational efficiency, ensuring a safer and more productive working environment.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский عربى
عربى