The Ultimate Guide to HPL Cleanroom Doors: Everything You Need to Know
Introduction to HPL Cleanroom Doors
What are Cleanroom Doors?
Cleanroom doors are specialized doors designed to meet the stringent requirements of controlled environments where factors like dust, airborne particles, and microbial contamination must be minimized. These doors are commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, microelectronics, and food processing, where maintaining air quality and contamination control is crucial. Unlike standard doors, cleanroom doors are engineered to create a tight seal and prevent contamination from entering or exiting a cleanroom space, ensuring that the environment remains sterile and controlled.
The construction of cleanroom doors varies, but they are typically made from materials that are durable, resistant to chemicals, and easy to clean. Depending on the specific requirements of the cleanroom, these doors can also be equipped with additional features such as automatic door systems, interlock mechanisms, or view panels.
What is HPL (High-Pressure Laminate)?
High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) is a composite material made by fusing multiple layers of paper or fabric with resin under high heat and pressure. The result is a dense, durable, and non-porous surface that is resistant to damage, wear, and chemical exposure. HPL is commonly used in various applications, including wall cladding, countertops, and, as we’ll explore here, cleanroom doors.
HPL is valued for its excellent durability, smooth surface, and ease of maintenance, making it an ideal material for cleanroom doors that need to withstand constant cleaning, harsh chemicals, and potential physical impacts. Moreover, it is customizable in terms of texture and finish, allowing it to meet both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Why Use HPL in Cleanroom Doors?
The use of HPL in cleanroom doors offers several advantages that are essential for maintaining the integrity of controlled environments. First, its non-porous nature helps to prevent the accumulation of contaminants such as dust, dirt, or bacteria. Since cleanroom environments demand regular cleaning and sanitization, HPL’s smooth surface ensures that it can be easily wiped down without harboring germs or residues.
Additionally, HPL cleanroom doors are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making them ideal for use in industries where exposure to corrosive substances is common. Whether it’s pharmaceutical production or semiconductor manufacturing, HPL provides the necessary durability to stand up to frequent cleaning and harsh chemical treatments.
Another benefit of HPL cleanroom doors is their versatility in design. Manufacturers can tailor the finish and color of HPL to meet the specific needs of the facility, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. Moreover, HPL doors are lightweight yet robust, offering a balance of structural integrity and ease of operation.
Benefits of HPL Cleanroom Doors
HPL cleanroom doors offer several key advantages that make them an excellent choice for controlled environments. Their combination of durability, resistance, ease of maintenance, and design flexibility makes them a popular option in various industries.
Durability and Longevity
One of the standout features of HPL cleanroom doors are their remarkable durability. The high-pressure lamination process results in a dense, robust surface that can withstand heavy use without showing signs of wear. Whether exposed to constant foot traffic, equipment movements, or minor impacts, these doors maintain their structural integrity and appearance over time. Their resistance to scratches and dents helps them maintain a clean and professional appearance, even in high-traffic areas.
This durability translates into a longer lifespan, meaning that businesses can enjoy the benefits of their HPL doors for many years, reducing the need for frequent replacements or costly repairs. In industries where operational downtime must be minimized, the long-lasting performance of HPL doors is an essential factor in ensuring smooth, uninterrupted operations.
Chemical Resistance
In cleanroom environments, the presence of chemicals is common, whether in manufacturing processes, cleaning agents, or even from airborne particles. HPL cleanroom doors are highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, solvents, and cleaning agents, which makes them ideal for use in industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and microelectronics.
The chemical resistance of HPL ensures that the doors will not degrade or suffer damage when exposed to harsh substances. This ability to withstand frequent chemical exposure without compromising their performance is critical in maintaining the integrity of cleanrooms, where contamination control is essential.
Cleanability and Hygiene
Maintaining cleanliness and hygiene is a top priority in cleanroom environments. HPL cleanroom doors are designed with smooth, non-porous surfaces that make them easy to clean and sanitize. Unlike wood or other porous materials, HPL does not absorb liquids or contaminants, which helps prevent the buildup of bacteria, mold, or other harmful microorganisms.
Regular cleaning is essential to maintaining the sterile environment of the cleanroom, and HPL doors can be wiped down quickly and thoroughly without the risk of damaging the surface. Their resistance to staining and discoloration also ensures that they maintain a pristine, hygienic appearance even after multiple cleanings.
Design Flexibility
HPL cleanroom doors offer significant design flexibility, allowing manufacturers to tailor the appearance and functionality of the doors to meet specific requirements. The laminate surfaces can be customized with a variety of finishes, textures, and colors to suit the aesthetic needs of the facility while still maintaining the essential cleanroom characteristics.
In addition to aesthetic customization, HPL doors can be manufactured in various sizes and configurations, such as flush, airtight, or sliding doors, to suit the operational needs of the cleanroom. This design versatility ensures that HPL cleanroom doors can be used in a wide range of applications, from small laboratories to large-scale manufacturing plants.
Cost-Effectiveness
While HPL cleanroom doors offer a range of premium features, they are often more cost-effective than other specialized cleanroom door options, such as stainless steel doors. The cost-effectiveness of HPL doors is due to the affordability of the raw materials and the efficient manufacturing process.
This makes them an attractive option for businesses looking to balance quality with budget constraints. Furthermore, their long lifespan, resistance to damage, and minimal maintenance requirements mean that the overall cost of ownership remains low, making HPL cleanroom doors a wise investment for facilities seeking both performance and value.
Applications of HPL Cleanroom Doors
HPL cleanroom doors are versatile and can be used in various industries where controlled environments are necessary. From pharmaceuticals to food processing, these doors play a vital role in maintaining sterile conditions and preventing contamination. Below are some key industries where HPL cleanroom doors are commonly used:
Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms
In the pharmaceutical industry, maintaining a clean and sterile environment is critical for the production of medications and other health-related products. HPL cleanroom doors help ensure that pharmaceutical cleanrooms meet the strict requirements of regulatory bodies such as the FDA and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices). The chemical resistance, durability, and ease of cleaning that HPL doors offer are essential in preventing contamination during the manufacturing process. These doors also contribute to maintaining the required air pressure and contamination levels, ensuring product integrity and safety.
Microelectronics Cleanrooms
The microelectronics industry, including semiconductor manufacturing, requires highly controlled environments where even the smallest particle can compromise the quality and functionality of the products. HPL cleanroom doors are an excellent choice for microelectronics cleanrooms due to their ability to provide a tight seal, preventing the entry of dust and particles. Their resistance to chemical exposure, particularly from solvents and acids used in the production process, ensures that these doors remain effective throughout their lifespan in high-tech environments.
Biotechnology Cleanrooms
Biotechnology companies rely on cleanroom environments to conduct research, development, and manufacturing of biologics, medical devices, and other sensitive products. HPL cleanroom doors provide a combination of durability, hygiene, and contamination resistance necessary for these environments. Additionally, biotechnology cleanrooms often have specific design requirements related to airflow, sealing, and pressure control, all of which can be effectively managed with HPL doors. Their customizable features allow for integration into complex cleanroom systems that are essential for successful biotechnology operations.
Food Processing Cleanrooms
In food processing, cleanliness and hygiene are paramount to ensure product safety and quality. Cleanrooms are used in food production facilities to limit exposure to contaminants that could compromise food safety. HPL cleanroom doors are an ideal solution for these environments because of their easy-to-clean surfaces, resistance to chemicals used in cleaning, and ability to create a tight seal to protect the integrity of the cleanroom environment. These doors are also resistant to the various food acids and other chemicals that may be present during the processing phase.
Other Controlled Environments
In addition to the industries mentioned above, HPL cleanroom doors are also used in a variety of other controlled environments where contamination control is essential. These may include laboratories, research facilities, aerospace manufacturing, and medical device production. HPL doors help ensure that these environments remain sterile and that contaminants are kept at bay, no matter the specific industry. Their versatility and adaptability make them a go-to choice for any facility that requires high levels of cleanliness and contamination control.
Types of HPL Cleanroom Doors
HPL cleanroom doors come in various configurations and styles, each tailored to specific needs and applications within cleanroom environments. The choice of door type largely depends on factors such as traffic volume, level of airtightness required, space constraints, and the intended use of the cleanroom. Below are the most common types of HPL cleanroom doors:
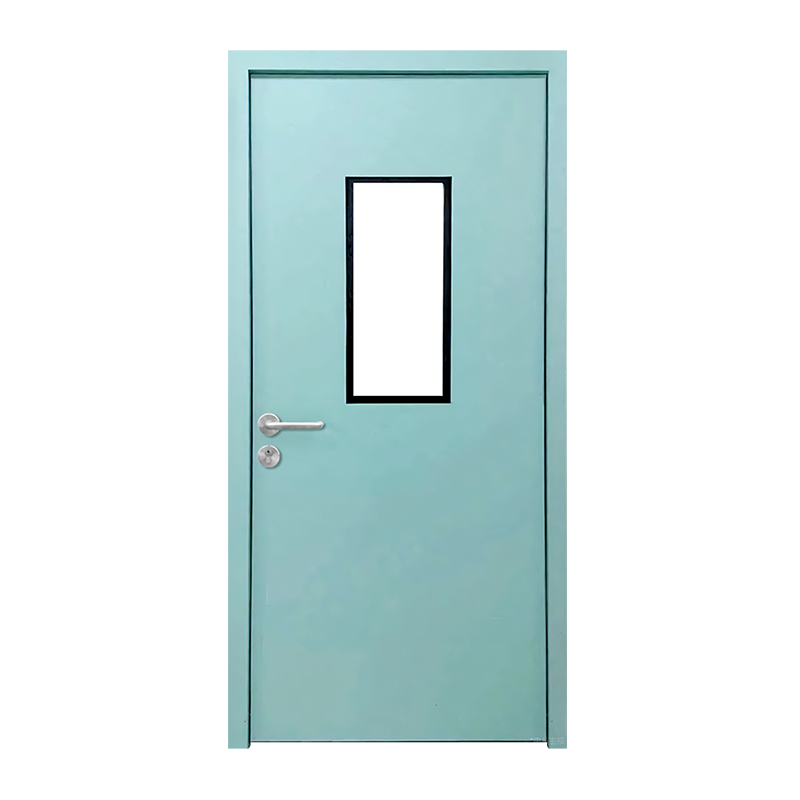
Flush Doors
Flush doors are one of the most commonly used door types in cleanroom environments due to their smooth, flat surfaces. They are designed with a continuous surface that minimizes the chance of dust, dirt, and contaminants accumulating in gaps or grooves. Flush HPL doors are ideal for areas that require frequent cleaning and where hygiene is of the utmost importance. Their seamless design also enhances their ability to maintain a proper seal, further contributing to contamination control.
Airtight Doors
Airtight doors are specifically designed for environments that require a high level of air pressure control, such as pharmaceutical and biotechnology cleanrooms. These doors are equipped with advanced sealing mechanisms, such as gasket seals or compression systems, to prevent air leakage. Airtight HPL cleanroom doors help maintain the controlled atmosphere within the cleanroom, preventing external contaminants from entering and ensuring that the cleanroom environment meets the required ISO standards.
Airtight doors are particularly beneficial in areas where contamination risks are heightened, such as sterile manufacturing environments or labs working with highly sensitive substances. Their ability to seal tightly and maintain pressure is crucial in preventing contamination.
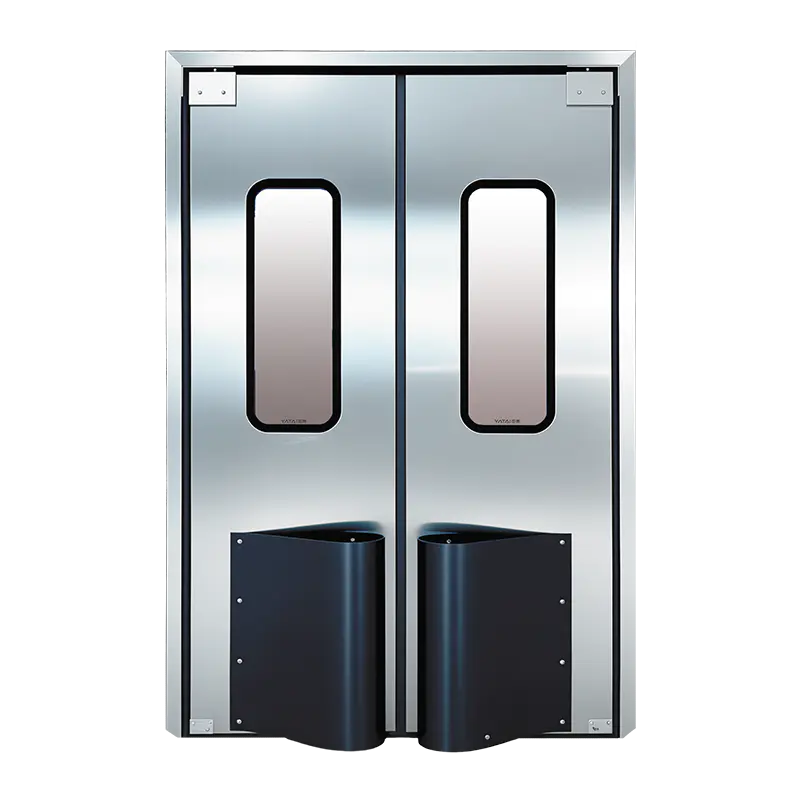
Swing Doors
Swing doors, also known as hinged doors, are another common option for cleanroom applications. They are typically mounted on hinges and open by swinging outward or inward, depending on the design. Swing doors can be used in cleanrooms with moderate traffic volumes where quick and easy access is required.
HPL swing doors are designed to minimize the buildup of dirt and germs, offering easy-to-clean surfaces while maintaining the integrity of the controlled environment. They are often chosen for spaces that don’t require the high-speed operation of automatic or sliding doors, such as smaller labs or storage areas within cleanroom facilities.
Sliding Doors
Sliding doors are ideal for cleanroom environments where space efficiency is important. These doors do not swing open like traditional doors; instead, they slide horizontally along a track, which makes them an excellent choice for areas where there may not be enough space for a traditional swinging door to open fully. Sliding HPL cleanroom doors are commonly used in high-traffic areas or where automation is needed to reduce manual interaction with the door.
In addition to their space-saving capabilities, sliding doors can be designed to be airtight or even automated, making them an excellent choice for facilities requiring high contamination control and ease of access.
Manual vs. Automatic Doors
Another consideration when choosing HPL cleanroom doors is whether to use manual or automatic doors. Manual doors are operated by hand, requiring individuals to open and close them physically. These doors are typically used in areas with less foot traffic or in smaller cleanrooms where automated systems may not be necessary. Manual doors are usually more affordable, simpler to maintain, and don’t require complex electrical or mechanical systems.
On the other hand, automatic doors are often used in cleanrooms with higher traffic or in areas where hands-free operation is essential for maintaining sterility. Automatic HPL doors can be equipped with sensors that open and close the door without physical contact, reducing the risk of contamination and improving workflow efficiency. These doors can also be integrated with interlock systems, ensuring that one door is closed before another opens to maintain a sealed environment.
Cleanroom Standards and HPL Doors
Cleanrooms must comply with various industry standards to ensure they meet the required levels of cleanliness, contamination control, and operational safety. These standards are crucial for industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and microelectronics, where even the smallest particles can lead to contamination or product defects. When selecting HPL cleanroom doors, it’s essential to ensure that they meet the necessary standards to maintain the integrity of the cleanroom environment.
ISO Classifications and HPL Doors
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides classifications for cleanrooms based on the level of airborne particles allowed in the environment. These ISO classifications range from ISO 1 (the highest level of cleanliness) to ISO 9 (the least clean). Each class specifies a maximum particle count per cubic meter, and the cleanroom must maintain this threshold at all times to prevent contamination.
HPL cleanroom doors play an integral role in maintaining these standards. The design of the doors, including airtight seals, smooth surfaces, and resistance to chemical agents, helps ensure that cleanroom conditions are maintained. The correct door type can help meet specific ISO classifications by preventing the introduction of particles and contaminants from outside or through door openings.
When designing or selecting doors for cleanrooms, manufacturers need to consider the required ISO class and ensure the doors’ sealing, durability, and performance align with those requirements.
GMP Requirements and HPL Doors
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are a set of regulations that ensure the quality and safety of products, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. These regulations are designed to minimize contamination risks and ensure consistent production quality. GMP guidelines cover a wide range of factors, including environmental conditions, equipment maintenance, personnel hygiene, and facility design.
HPL cleanroom doors must meet GMP standards to ensure they are suitable for regulated industries. The doors must provide a tight seal, be easy to clean, and resist chemical degradation from cleaning agents and environmental factors. Additionally, they must be able to withstand the operational demands of these industries, such as high traffic or exposure to specialized equipment.
By selecting HPL doors that meet GMP requirements, businesses ensure that their cleanroom environments maintain the highest levels of hygiene and quality control, helping them remain compliant with regulatory standards.
Other Relevant Standards
In addition to ISO and GMP standards, there are other relevant cleanroom regulations that HPL cleanroom doors must comply with, depending on the industry and location. For example, the U.S. FDA (Food and Drug Administration) has specific requirements for cleanroom environments in the pharmaceutical industry. Similarly, the European Union has its own set of guidelines for cleanroom operations under EU GMP guidelines.
Additionally, cleanroom doors may need to comply with safety regulations such as fire codes or electrical safety standards, particularly when automatic or sliding doors are involved. Fire-rated HPL doors may be required in certain environments to prevent the spread of fire in case of an emergency.
Ensuring that HPL cleanroom doors meet these various standards is crucial for facility managers looking to maintain compliance and minimize the risk of contamination.
HPL Cleanroom Door Specifications
When selecting HPL cleanroom doors, it’s essential to consider various specifications to ensure the doors meet the specific needs of your cleanroom environment. These specifications affect the performance, durability, and overall effectiveness of the doors in maintaining a sterile and controlled atmosphere. Below are the key specifications to keep in mind when choosing HPL cleanroom doors.
Material Thickness and Density
The material thickness and density of HPL play a significant role in determining the strength and insulation properties of the cleanroom door. Typically, HPL cleanroom doors are constructed with multiple layers of laminate to achieve the required thickness and durability. The density of the HPL material ensures that the door can withstand impact, resist damage, and maintain its structural integrity under high-traffic conditions.
A thicker, denser door also offers better sound insulation and thermal resistance, which can be crucial in certain cleanroom applications. It helps maintain the desired environmental conditions by preventing external temperature fluctuations and sound disturbances from affecting sensitive operations within the cleanroom.
Surface Finish and Texture
The surface finish and texture of HPL cleanroom doors are essential for both functional and aesthetic reasons. A smooth, non-porous finish is critical for preventing the buildup of dirt, dust, or bacteria, ensuring that the door can be easily cleaned and sanitized. A polished or matte finish is often selected for cleanroom doors, with the finish being both durable and resistant to staining.
The texture of the door surface can also affect its slip resistance and overall ease of cleaning. Some applications may require a textured finish to improve grip or safety, while others may prioritize a smooth, easy-to-wipe surface to maintain cleanliness.
Custom finishes and textures can be selected based on the design needs of the facility, ensuring the doors blend seamlessly with the overall aesthetics of the cleanroom while maintaining their high-performance standards.
Dimensions and Sizes
Cleanroom doors come in a variety of sizes to accommodate different facility layouts and traffic volumes. When selecting an HPL cleanroom door, it’s important to choose the correct dimensions to ensure a proper fit for the opening and functionality of the cleanroom. Custom sizing is often available to meet specific requirements.
In addition to the width and height, the thickness of the door frame should be considered, particularly if the door is required to provide additional insulation or airtightness. The frame design must also account for factors such as pressure differentials, especially in controlled environments where airflow is critical.
Fire Resistance
Depending on the regulations and the specific cleanroom application, fire resistance may be an important specification for HPL cleanroom doors. Some cleanrooms, particularly those in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, or food processing industries, may be required to have fire-rated doors to prevent the spread of fire within the facility.
HPL doors can be constructed with fire-resistant cores and materials to meet fire safety standards. These doors are tested to ensure they can withstand high temperatures for a specified duration, ensuring that they help protect the cleanroom in the event of a fire and maintain the safety of the personnel and materials inside.
Chemical Resistance
The chemical resistance of an HPL cleanroom door is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the cleanroom environment, especially in industries where exposure to harsh chemicals or solvents is common. HPL doors are designed to resist a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, solvents, and cleaning agents, without degrading or losing their structural integrity.
The chemical resistance of the door ensures that it will not be affected by routine cleaning procedures or by accidental spills of chemicals within the cleanroom. This is particularly important in industries such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, where contamination from cleaning agents or other chemicals could compromise product quality or research integrity.
Cleanroom Door Hardware and Accessories
The functionality and performance of HPL cleanroom doors are not solely determined by the door itself but also by the various hardware components and accessories that complement it. These components ensure that the doors operate efficiently, maintain the cleanroom’s sterile conditions, and meet specific operational needs. Below are key hardware and accessories commonly used with HPL cleanroom doors.
Door Handles and Locks
Door handles and locks are essential for controlling access to cleanroom environments while ensuring security and ease of operation. In cleanrooms, it is important that door handles are designed to prevent contamination. Stainless steel or other non-porous materials are often used for handles, as they are durable, easy to clean, and resistant to bacteria growth.
For sensitive environments, locks may be equipped with interlocking systems to control access. These systems ensure that one door cannot open while another remains open, maintaining pressure differentials and preventing cross-contamination. For higher security, keycard or biometric access systems may also be used to restrict entry to authorized personnel only.
Hinges and Closers
Hinges and closers are integral to the smooth operation of cleanroom doors, particularly for swing doors. High-quality, rust-resistant hinges are necessary to ensure that the door operates smoothly, with no risk of deterioration or contamination from corrosion. The hinges should also be easy to clean and maintain, as any buildup in the hinge area can negatively affect the door’s performance and hygiene.
Door closers, which automatically close the door after it is opened, are another key component in maintaining the cleanroom’s integrity. These devices help ensure that doors remain closed when not in use, preventing air leakage and contamination from entering the cleanroom. Adjustments to the speed and force of door closers can be made to suit the specific needs of the cleanroom.
Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets are critical in ensuring that HPL cleanroom doors maintain airtight and dust-tight properties. These components form a barrier between the door and the frame, preventing air, dust, or contaminants from entering the cleanroom. High-quality seals and gaskets are made from materials that are resistant to chemicals, temperature variations, and wear over time.
The type of seal required will depend on the cleanroom’s specific needs, including whether the room needs to maintain positive or negative pressure. Proper sealing ensures that the controlled environment remains intact and that the cleanroom continues to meet the required ISO standards.
View Panels
View panels are an optional feature on HPL cleanroom doors that allow personnel to see into or out of the cleanroom without opening the door. These panels are typically made of tempered glass or polycarbonate materials that are easy to clean and resistant to scratching or clouding.
In environments where it’s important to maintain visibility, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing or laboratories, view panels help operators monitor the situation without compromising the integrity of the cleanroom. These panels can also help improve safety by providing clear sightlines and preventing accidents or unnecessary door openings.
Interlock Systems
Interlock systems are designed to prevent two cleanroom doors from being opened at the same time, maintaining the required pressure differential and ensuring that contaminants are not introduced. This system is often used in environments where a high level of contamination control is necessary, such as in sterile pharmaceutical manufacturing or medical device production.
Interlock systems can be mechanical, electrical, or even automated, and they can be integrated with sensors and automatic door operators to streamline operations. The interlock mechanism ensures that cleanroom conditions are not compromised by accidental or simultaneous door openings.
Automatic Door Operators
Automatic door operators are ideal for cleanroom environments where hands-free operation is crucial to minimize contamination. These operators can be activated by motion sensors, touchless buttons, or even RFID cards. Automatic door systems provide seamless, contactless access, reducing the need for personnel to physically touch the door handles, which could introduce contaminants.
These systems can be integrated with other features, such as interlocks or pressure-sensitive controls, to ensure that the cleanroom remains sealed and maintains the necessary air quality standards. Automatic doors are also useful in high-traffic areas, providing easy access while minimizing human error and operational disruptions.
Installation of HPL Cleanroom Doors
Proper installation of HPL cleanroom doors is crucial to ensure that they function correctly, maintain the integrity of the controlled environment, and comply with necessary standards. A poorly installed door can lead to air leaks, contamination, and even safety hazards. Below are the key steps involved in the installation process for HPL cleanroom doors.
Preparing the Opening
The first step in installing HPL cleanroom doors is to prepare the door opening. It’s essential that the opening is properly measured to ensure that the door will fit correctly. Accurate measurements of the height, width, and depth of the door frame are crucial to avoid installation delays or the need for modifications.
The surface around the door frame must also be clean and level, as any inconsistencies can affect the door’s alignment and performance. The installation area should be free from debris, dust, or any other contaminants that could interfere with the door’s function or seal.
Mounting the Door Frame
Once the opening is prepared, the next step is to mount the door frame. The frame must be securely anchored to the wall structure using appropriate fasteners and adhesives to ensure that it remains firmly in place. The frame must be aligned correctly to ensure that the door swings or slides smoothly and seals properly when closed.
In cleanroom environments, it’s crucial that the frame is mounted without creating any gaps between the door and the wall. This will prevent air leaks and ensure that the cleanroom’s pressure differential is maintained.
Installing the Door Leaf
With the frame in place, the next step is to install the door leaf, which is the actual door that swings, slides, or opens to provide access. The door leaf must be carefully mounted onto the frame using hinges, tracks, or other mounting hardware, depending on the type of door.
If the door is a swing door, ensure that the hinges are positioned properly to allow for smooth operation. For sliding doors, check that the tracks are securely installed and that the door moves easily. Additionally, any view panels or special features, such as interlock systems or seals, should be integrated during this step.
Sealing and Adjustments
After the door leaf is installed, the next step is to seal the door properly. Seals and gaskets around the door frame should be inspected and installed to ensure that there are no gaps where air or contaminants can enter the cleanroom. If the door is intended to be airtight, special attention must be given to the compression of seals to guarantee that the door forms a perfect seal when closed.
Any necessary adjustments to the door’s operation should also be made at this stage. For example, adjusting the door closer’s speed or ensuring the door opens and closes smoothly without binding.
Testing and Certification
After installation, the cleanroom door must undergo testing to ensure that it meets the required specifications. This includes testing for airtightness, proper sealing, and functionality of automatic systems or interlocks. Pressure tests are often conducted to ensure that the door does not allow air to escape, particularly in environments that require precise pressure control.
Once testing is completed and the door passes all requirements, certification can be provided to confirm that the installation meets all necessary cleanroom standards, such as ISO classifications and GMP guidelines. This certification is essential for regulatory compliance and ensuring the door’s effectiveness in maintaining cleanroom conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning of HPL Cleanroom Doors
To ensure the continued performance and cleanliness of HPL cleanroom doors, regular maintenance and cleaning are essential. Proper care helps maintain the integrity of the door, ensuring that it functions as intended, seals correctly, and contributes to the overall cleanliness of the controlled environment. Below are the key aspects of maintaining and cleaning HPL cleanroom doors.
Regular Cleaning Procedures
Regular cleaning is crucial to prevent the accumulation of contaminants on the surface of the door and frame. The frequency of cleaning depends on the type of cleanroom and the level of contamination risk. For high-traffic areas or facilities dealing with sensitive materials, doors may need to be cleaned daily or several times a week.
The general cleaning procedure for HPL cleanroom doors involves wiping down the door surfaces with a damp cloth to remove dust, dirt, and debris. Special care should be taken around the door seals and hinges, as these areas can accumulate dirt or chemical residues. In environments where contamination is a major concern, it is also essential to clean the door frame and any hardware regularly to prevent contamination from spreading.
Recommended Cleaning Agents
When cleaning HPL cleanroom doors, it’s important to use cleaning agents that are safe for both the material and the cleanroom environment. Abrasive cleaners or harsh chemicals can damage the surface of the HPL and compromise the door’s ability to maintain a sterile environment.
Mild detergents or disinfectants are typically recommended for cleaning HPL cleanroom doors. For general cleaning, a mixture of water and a neutral pH cleaner should suffice. For more thorough sanitization, isopropyl alcohol or other non-corrosive, non-abrasive agents can be used. Always ensure that the cleaning agents are compatible with HPL material to prevent any long-term damage to the door surface.
Inspection and Repair
In addition to regular cleaning, HPL cleanroom doors should be inspected periodically to ensure they are functioning correctly. This includes checking for any visible signs of wear and tear, such as cracks, dents, or damage to the surface finish. Inspect the door seals and gaskets to ensure they are intact and properly compressed, as gaps can lead to contamination.
Hardware such as hinges, locks, and closers should also be inspected to ensure they are working smoothly and have not been damaged. Any issues, such as a door not closing properly or hardware that has become loose, should be addressed immediately to prevent the door from compromising the cleanroom’s integrity.
If any part of the door is damaged or showing signs of wear, it should be repaired or replaced promptly. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can extend the life of the door and help avoid costly replacements in the future.
Preventing Contamination
Maintaining cleanliness not only involves cleaning but also taking preventive measures to reduce contamination risks. One of the most important steps in contamination control is ensuring that the door seals remain intact. If the seals are damaged or worn out, they should be replaced immediately, as any gap in the seal can allow contaminants to enter the cleanroom.
Furthermore, staff operating the doors should follow best practices to avoid introducing contaminants into the cleanroom. This includes ensuring that doors are only opened when necessary and minimizing the frequency of door openings. In areas where automatic or sliding doors are used, ensure that they are properly calibrated to open and close as needed without compromising the cleanroom’s pressure balance.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский عربى
عربى