Steel Cleanroom Doors: Design, Performance Standards, and Installation Best Practices for Controlled Environments
Understanding the Role of Steel Cleanroom Doors in Contamination Control
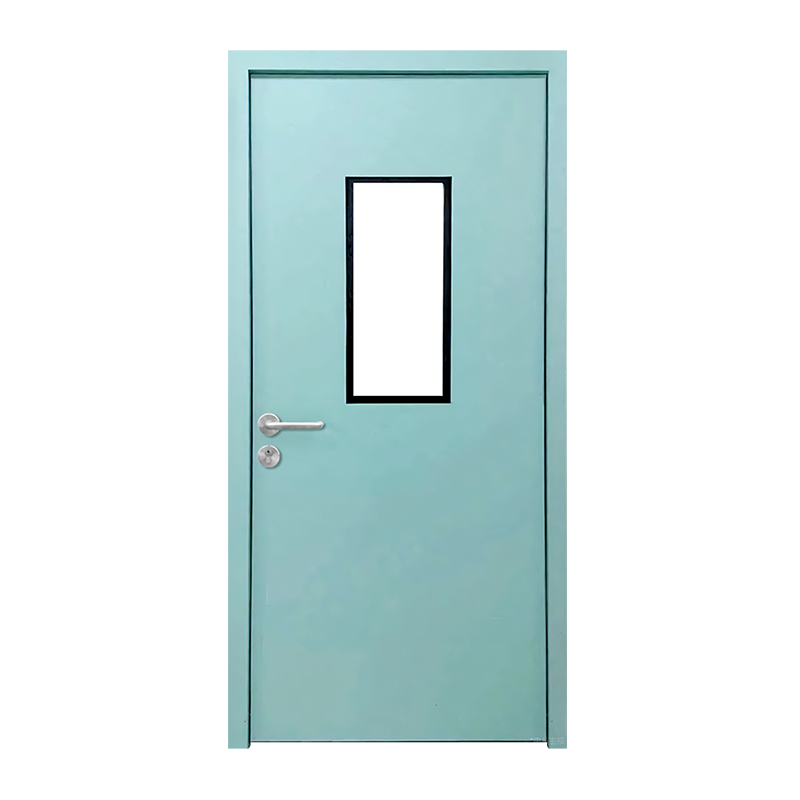
A steel cleanroom door is a critical barrier designed to maintain sterile conditions by preventing particulate intrusion, airflow leakage, and microbial contamination. These doors are engineered for environments where precision hygiene and air pressure control are essential, including pharmaceutical manufacturing, biotechnology labs, hospitals, semiconductor facilities, and food processing plants.
Unlike conventional doors, cleanroom steel doors are built with seamless surfaces, chemical-resistant finishes, and tight-sealing mechanisms. Their durability supports frequent sanitization without corrosion or degradation, helping facilities comply with strict regulatory standards such as GMP, ISO 14644, and FDA cleanliness requirements.
Key Design Features of High-Performance Steel Cleanroom Doors
Seamless Construction for Hygiene
Steel cleanroom doors use smooth welded joints and minimal crevices to prevent particle accumulation. This design supports rapid cleaning cycles and minimizes contamination risks from dust or microbial growth.
Airtight Sealing Systems
Advanced gasket systems maintain positive or negative pressure differentials between rooms, which is essential for preventing cross-contamination in sterile environments.
Chemical and Impact Resistance
Powder-coated or stainless steel finishes resist disinfectants, solvents, and abrasion, ensuring longevity even in high-traffic cleanroom corridors.
- Flush surface panels for particle-free cleaning
- Integrated observation windows with double glazing
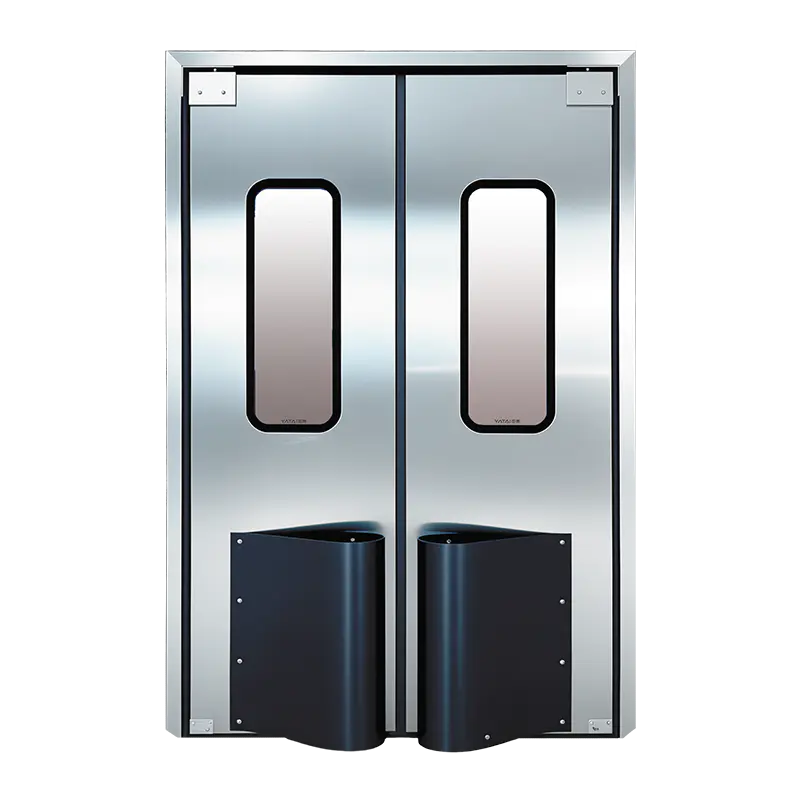
- Automatic sliding or swing mechanisms
- Antimicrobial coating options
Applications Across Critical Industries
Steel cleanroom doors are used wherever air purity and surface sanitation are mission-critical. Their adaptability allows integration into both modular cleanroom systems and permanent facility builds.
| Industry | Purpose of Steel Cleanroom Doors | Key Requirements |
| Pharmaceutical | Protect sterile drug manufacturing zones | Airtight seals, GMP compliance |
| Biotechnology | Control contamination in research labs | Chemical resistance, smooth finishes |
| Hospitals | Maintain isolation rooms and surgical areas | Antimicrobial surfaces, air pressure control |
| Electronics | Prevent dust in semiconductor production | Static control, tight sealing |
| Food Processing | Ensure hygienic production zones | Washdown resistance, corrosion-proof steel |
Choosing the Right Steel Cleanroom Door System
Door Operation Type
Sliding doors are ideal for space efficiency and airflow control, while swing doors offer simpler installation and lower maintenance for smaller cleanrooms.
Material Grade
Galvanized steel is cost-effective for controlled environments, while stainless steel is preferred in corrosive or sterile zones requiring aggressive sanitization.
Compliance Certification
Ensure door systems meet ISO cleanroom classifications and local regulatory standards. Proper documentation simplifies inspections and audits.
- Verify airtight performance ratings
- Select compatible automation systems
- Confirm cleanroom class compatibility
Installation Best Practices for Cleanroom Door Integrity
Proper installation is just as important as door quality. Incorrect alignment or sealing gaps can compromise airflow control and cleanliness levels.
Structural Integration
Doors should be installed flush with cleanroom wall panels to eliminate ledges that trap contaminants.
Pressure Testing
Post-installation air leakage testing ensures compliance with cleanroom pressure standards.
Automation Calibration
Automatic doors must be calibrated for smooth operation to avoid air turbulence and wear.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance Management
Regular maintenance extends door lifespan and ensures consistent cleanroom performance. Steel cleanroom doors are low maintenance but require scheduled inspections.
- Inspect seals for wear and compression loss
- Clean surfaces with approved disinfectants
- Lubricate sliding mechanisms
- Test automation sensors quarterly
Future Trends in Steel Cleanroom Door Technology
Innovations in cleanroom door systems are focusing on improved energy efficiency, smart monitoring, and enhanced hygiene automation.
Emerging solutions include touchless access systems, real-time pressure monitoring, self-sanitizing surface coatings, and integration with cleanroom management software for contamination tracking.
- IoT-enabled door performance tracking
- UV sterilization integration
- Energy-saving airflow optimization
Why Steel Cleanroom Doors Deliver Long-Term Value
Although initial costs may exceed standard industrial doors, steel cleanroom door systems provide superior lifecycle value. Their durability, regulatory compliance, and contamination protection reduce operational risks and downtime.
By maintaining consistent environmental control, facilities protect product quality, improve audit outcomes, and support scalable cleanroom expansions.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский عربى
عربى